STEM CELLS AUTOLOGICAL EXPORT SYSTEMS
WHAT ARE STEM CELLS?
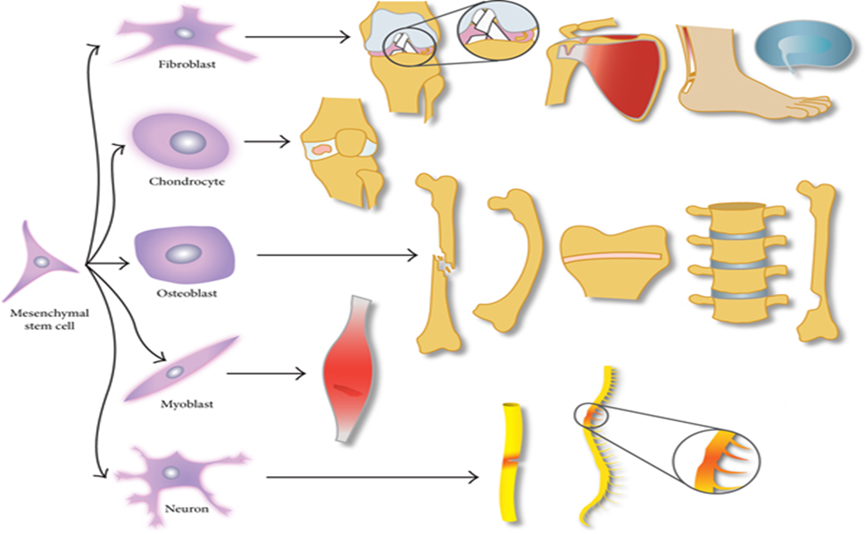
These are initial ("primordial") undifferentiated cells of the body.
Primordial stem cells have the ability to differentiate according to the needs of the organism, in order to form the basis for the healing - regeneration of various tissues.
They are generally divided into embryonic stem cells obtained from the umbilical cord at birth and adult stem cells.
Adult primordial stem cells are stored in various tissues in dormancy and are activated when needed.
In adults Stem cells are found in:
1. At Bone marrow / MAGELLAN System.
2. At Fatty tissue / MyStemX2 System.
A little history
In 1867, the German pathologist Cohnheim hypothesised that non-haematopoietic cells derived from the bone marrow could migrate through the bloodstream to distant sites of injury and participate in tissue regeneration.
In 1868, the French physiologist Goujon studied the osteogenic potential of bone marrow in rabbits. Friedenstein demonstrated the existence of a non-hematopoietic stem cell in bone marrow more than a hundred years later. Following this discovery, research on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) explored their therapeutic potential.
Recently, Japanese scientist (first orthopaedic surgeon) Shinya Yamanaka demonstrated that introducing a small set of transcription factors into a differentiated cell was enough to restore the cell to a pluripotent state. Yamanaka shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and opened a new door for potential applications of MSCs.
*Bone transplantation and tissue engineering, part IV. Mesenchymal stem cells: history in orthopedic surgery from Cohnheim and Goujon to the Nobel Prize of Yamanaka, 2015 Apr;39(4):807-17. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2716-8. Epub 2015 Mar 7.
Philippe Hernigou, Orthopedic Surgery, Hopital Henri Mondor, Créteil, France
Clinical applications
The treatment with autologous blastocysts has been applied for over 20 years for the treatment of various diseases by many medical specialties:

Orthopaedics

Plastic surgery

Vascular surgery

Surgery

Maxillofacial surgery

Ophthalmology

Urology

Neurosurgery
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY SOLUTIONS FROM MEDISPORTS
Our company has a complete portofolio of materials as well as the necessary accompanying equipment.
The systems are certified by the American FDA, the European agencies and the EOF.


